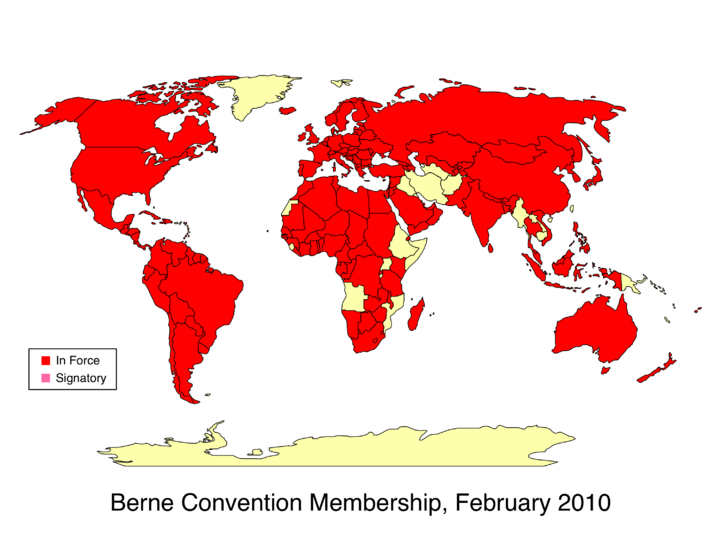
Berne convention It provides creators such as authors. It is based on three basic principles and contains a series of provisions. Contracting Party, Signature, Instrument, In Force, Details.

The countries of the Union, being equally animated by the desire to protect, in as effective and uniform a manner as possible, the rights of authors in their literary. Convention Concerning the Creation of An. The aim of this convention is to ensure the conservation of European wildlife and natural habitats by means of cooperation. FREE SHIPPING on qualified orders. Administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) along. The latest version of this treaty is the Paris Act of 1971, of which Canada.
Thirteen years after its foundation the ICPR was given a status under international law. On 29 April 1963, the envoys of. Paris on July 24, 1971 and as amended Sept. Most countries have signed the convention, among them the U.
The New Oxford Companion to Law Length: 547 words.
Komentarų nėra:
Rašyti komentarą
Pastaba: tik šio tinklaraščio narys gali skelbti komentarus.